The functions of the processor
the CPU is similar to human brain. Every single operation that you do with your computer is processed in the CPU. The performance of your computer is based upon simple mathematical operations and the CPU is the device that controls all of those operations. Let's say we are using a calculator to add two numbers. You enter the numbers using your keyboard. The keyboard controller turns all of that information into binary code. Binary code consist of sequences of 0 and 1. This information is this sent to the registry and then transferred to the CPU. The CPU has an integrated ALU (Arithmetical Logical Unit). The ALU is responsible for all mathematical and logical operations.
Some of the processors functions include:
- Performing calculations
- Data manipulation
- Decision making
- performance features
- Clock speed, cores, cache
- Makes
- Intel, AMD, ARM
- Overclocking
- Heat sinks – purpose, water cooled, air cooled
Functions of a motherboard
A motherboard is one of the most essential parts of a computer system. It holds together many of the crucial components of a computer, including the CPU, memory and connectors for the peripherals. The base of a motherboard consists of a very firm sheet of non-conductive material, typically some sort of rigid plastic. In addition to circuits, a motherboard contains a number of sockets and slots to connect the other components.
To understand how computers work, need to know some important parts of the motherboard and how the motherboard connects the various parts of a computer system together. Here are some of the typical parts:
- A CPU socket - the actual CPU is directly soldered onto the socket. Since high speed CPUs generate a lot of heat, there are heat sinks and mounting points for fans right next to the CPU socket.
- A power connector to distribute power to the CPU and other components.
- Slots for the system's main memory, typically in the form of DRAM chips.
- A chip forms an interface between the CPU, the main memory and other components. On many types of motherboards, this is referred to as the Northbridge. This chip also contains a large heat sink.
- A second chip controls the input and output (I/O) functions. It is not connected directly to the CPU but to the Northbridge. This I/O controller is referred to as the Southbridge. The Northbridge and Southbridge combined are referred to as the chipset.
- Several connectors, which provide the physical interface between input and output devices and the motherboard. The Southbridge handles these connections.
- Slots for one or more hard drives to store files. The most common types of connections are Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) and Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA).
- A read-only memory (ROM) chip, which contains the firmware, or startup instructions for the computer system. This is also called the BIOS.
- A slot for a video or graphics card. There are a number of different types of slots, including the Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) and Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe).
- Additional slots to connect hardware in the form of Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) slots.
Functions of the BIOS
A computer's Basic Input Output System and Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor together handle a rudimentary and essential process: they set up the computer and boot the operating system. The BIOS's primary function is to handle the system setup process including driver loading and operating system booting. The CMOS's primary function is to handle and store the BIOS configuration settings.
Functions of a Power Supply
to provide power to the PC in a low voltage direct current, converted from the wall sockets high voltage direct current. The power supply typically outputs voltages at 12v, 5v, 3.3v for the components of the PC. A higher-watt PSU can supply more power. Desktop power supplies have a power output rating of from 200 watts to 1800 watts (for ultra-high-end, enthusiast-class products). Wattage ratings higher than that would exceed the capabilities of a typical 15-ampere electrical outlet.Functions of Specialized Cards
Sound Cards
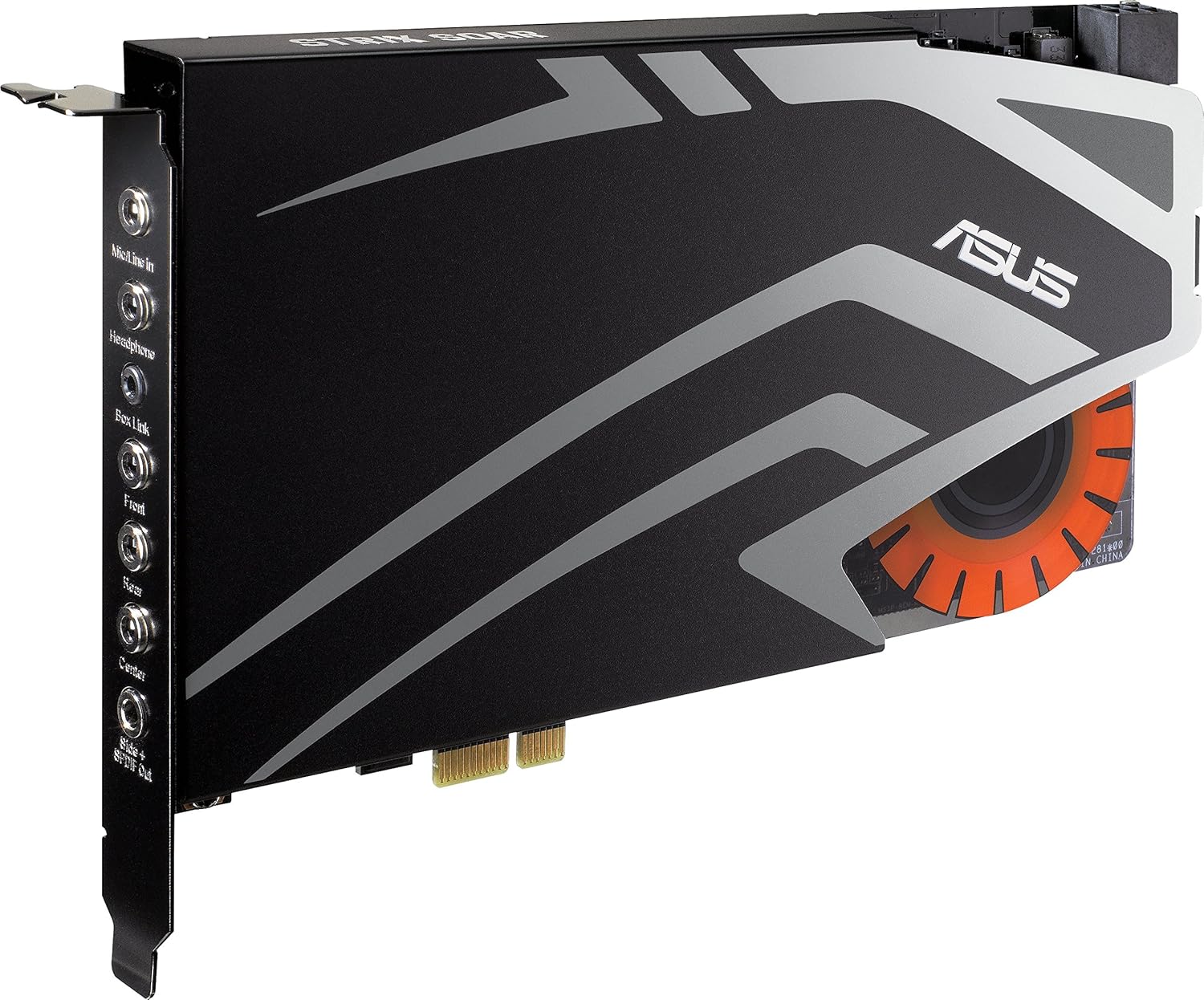 have extended sound capabilities, and for sound components to be used, for
have extended sound capabilities, and for sound components to be used, forexample headphones.
How it communicates with other components: The sound card translates analogue- to-digital waves to make the
sound heard on the computer, some sound cards use a coder/decoder chip also
called a CODEC which performs both functions
Graphics Cards
 Description of purpose: The graphics card is an adapter card that allows the computer to show graphics on the monitor.
Description of purpose: The graphics card is an adapter card that allows the computer to show graphics on the monitor.How it communicates with other components: The images that are shown on the monitor are made of tiny dots
called pixels. A screen displays over a million pixels and the computer has to
decide what to do with everyone in order to create an image, to do this it needs
graphics capability and that’s not possible without a graphics card, the
graphics card decides how to use the pixels on the screen to create an image and
then sends information to the monitor through the cable.
Network interface cards
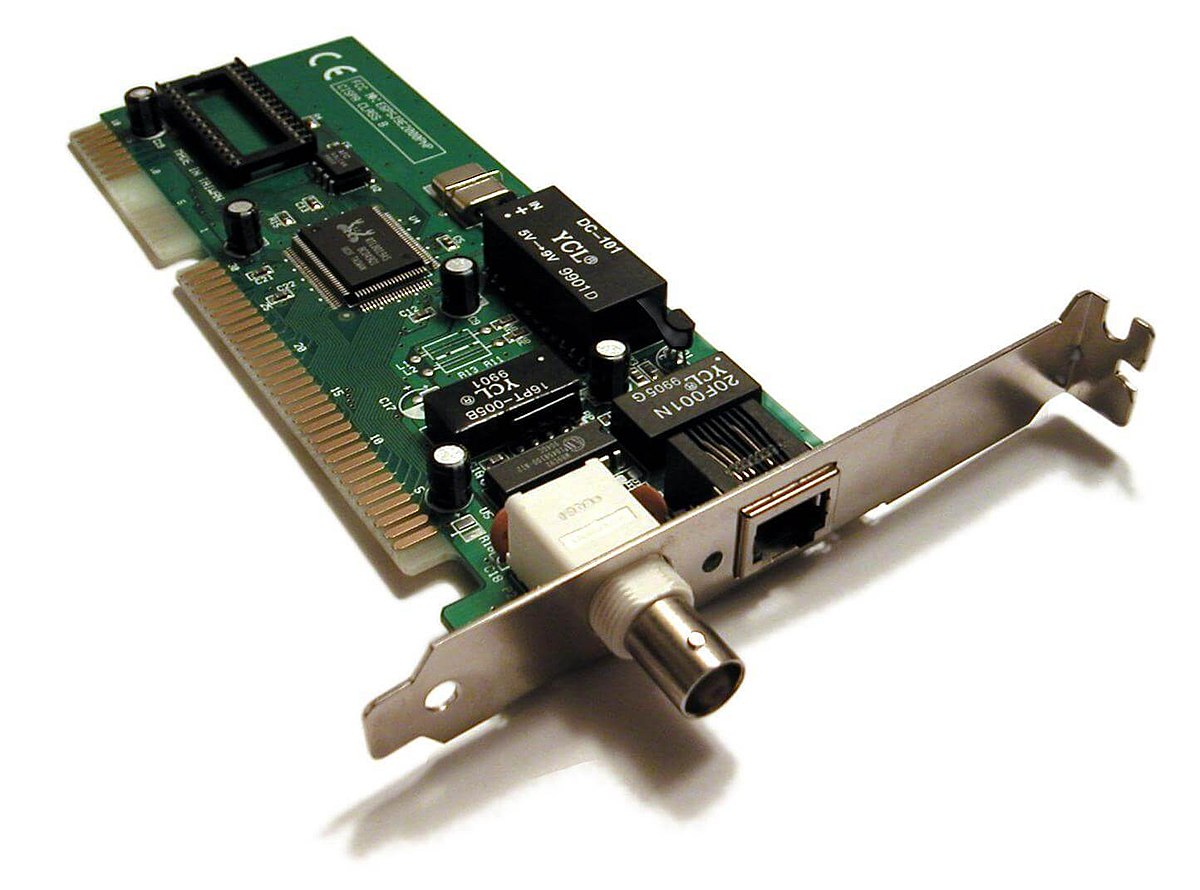 Description of purpose: The network interface card allows the computer to connect to a
Description of purpose: The network interface card allows the computer to connect to anetwork and access it wirelessly, It uses radio signals to do so. It is connected to the computer circuit board and provides a full-time wireless
connection to either a LAN (local area network) or WAN (wide area
network)
How it communicates with other components: It converts the data sent by the computer into a form which can
be used by the network cable, and then translates the data coming from the cable
into bytes so that the computer CPU can read it. Network interface card is very
important to link computers so data can be sent and receive via the LAN this is
basically the Ethernet card and will be installed in the computers slot.
Functions of a Hard Drive
A hard drive is a magnetised storage area. The Operating System is stored on the hard drive as well as all of the software programmes, for example, Microsoft Word. The hard drive is a few circular disks on top of each other. A little arm moves over the disks and writes things to these circular plates, and reads them. When a file is saved and a new folder is created, the information is sent to the circular plates. This basically is what a hard drive does.
The hard drive controller is typically found on the motherboard where you plug in the hard drives data connection. It controls the passing of data between the CPU and hard drive as well as between the RAM and hard drive. If the hard drive controller on your motherboard does not have the proper connector for your hard drive, an adapter can be used.
SATA stands for 'Serial Advanced Technology Attachment' or 'Serial ATA'. They are used for connecting host bus adapters for example the computer to mass storage devices such as hard drives. SATA cables are thin and long and includes 7-pins. They are now being used on most new computers.
IDE Stands for 'Integrated Drive Electronics'. This is a type of connection which is used to connect an optical drive and hard drive together as well as connecting them to the motherboard . Since the IDE was discovered it's capacity has massively increased from 20MB to 2TB .
EIDE stands for 'Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics'. It makes the computer and the storage driver have a standard electronic communication. It also allows for faster access to the hard drive.
Master/slave- The master drive responses to the commands and controls the slave drive. It's considered as the first drive and the slave drive is referred to as the second drive. As the slave drive controls the other devices.
Functions of Fans and Heat Sink
Computer fans are sometimes noisy and irritating, but they perform the very important function of cooling the computer, specifically the central processing unit. If this component reaches a pre-set temperature, the computer will shut down. This is called a "thermal check," and mainframes, servers and personal computers all have this protective feature built in.
 A heat sink is an electronic device that incorporates either a fan or a peltier device to keep a hot component such as a processor cool. There are two heat sink types: active and passive.
A heat sink is an electronic device that incorporates either a fan or a peltier device to keep a hot component such as a processor cool. There are two heat sink types: active and passive.
Active heat sinks utilize the power supply and are usually a fan type or some other peltier cooling device. If you are looking to purchase an active heat sink, we recommend purchasing fans with ball-bearing motors that often last much longer than sleeve bearings. Sometimes these types of heat sinks are referred to as an HSF, which is short for heat sink and fan.
Passive heat sinks are 100% reliable, as they have no mechanical components. Passive heat sinks are made of an aluminum-finned radiator that dissipates heat through convection. For passive heat sinks to work to their full capacity, there should be a steady airflow moving across the fins. The above picture is an example of a heat sink that is both active and passive.
Heat spreaders are another name for heat sinks and commonly used to describe the covers on computer memory that help dissipate the heat produced by the memory.
Functions of Ports
A port is a connector in a computer where you can connect an external device such as a printer, keyboard, scanner, mouse, or modem - (peripheral). This connection allows instructions and data to flow between the computer and the device. These computer ports are also commonly referred to as the Input and Output ports.A computer cable connector is the part of a cable that plugs into a port or interface to connect a device to the motherboard or another device. Most connectors are either male (containing one or more exposed pins) or female (containing holes in which the male connector can be inserted). A number of different connector types are used to connect various external devices to the computer.
Functions of Internal Memory
RAM is a fast volatile type of memory in which programs, the operating system, applications, the graphical user interface (GUI). If a computer loses power, all data stored in its RAM is lost.
ROM is memory that cannot be changed by a program or user. ROM retains its memory even after the computer is turned off. For example, ROM stores the instructions for the computer to start up when it is turned on again.
Cache is a specialized form of computer memory. In the case of Internet, "cache" is commonly used in the context of "browser cache" it is designed to speed up the computer by prioritizing its contents for quick access. cache holds copies of recently accessed data such as a web page and pictures on web pages. It keeps this data ready to "swap" onto your screen within fractions of a second. So, instead of requiring your computer to go to the original web page and photos in Denmark, the cache simply offers you the latest copy from your own hard drive. This caching-and-swapping speeds up page viewing because the next time you request that page, it is accessed from the cache on your computer instead of from the distant Web server.

